Budget 2021 Highlights, Summary & Data.
The Union budget 2021-22 was announced by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on 1st Feb in the parliament. In the 2021 budget, she focuses on the six pillars of reviving the economy.
- Health and Wellbeing
- Physical & Financial Capital Infrastructure
- Inclusive Development for Aspirational India
- Reinvigorating Human Capital
- Innovation and R&D
- Minimum Government and Maximum Governance
In this article, we go through all the Important announcements and Data produced by the Government.
Table Content
- Government Budget 2021 at a Glance
- Deficit Statistics
- Direct Tax Proposals
- Indirect Tax Proposals
- CGST Act was amended for several provisions as follows:
- Health
- Industry
- Infrastructure
- Urban Development
- Financial Reforms
- Agriculture and Fisheries
- Migrate Worker and Labour
- Education
- Research and Development
- Fiscal Position
- Related posts:
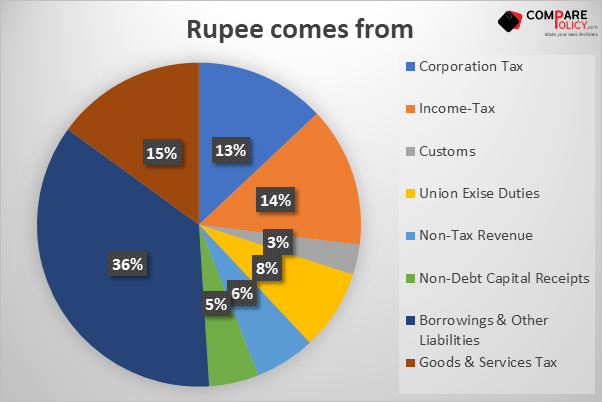
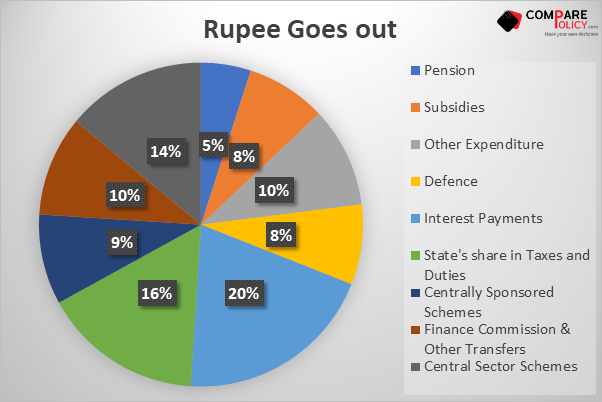
Government Budget 2021 at a Glance
(In Rs. crore)
| S.no | Particulars | Actuals 2019-2020 | Estimate Budget 2020-2021 | Revised Budget 2020-2021 | Budget Estimate 2021-2022 |
| 1 | Revenue Receipt | 1684059 | 2020926 | 1555153 | 1788424 |
| 2 | Tax Revenue (net to center) | 1356902 | 1635909 | 1344501 | 1545396 |
| 3 | Non-Tax Revenue | 327157 | 385017 | 210652 | 243028 |
| 4 | Capital Receipt | 1002271 | 1021304 | 1895152 | 1694812 |
| 5 | Recover of Loan | 18316 | 14967 | 14497 | 13000 |
| 6 | Other Receipts | 50304 | 210000 | 32000 | 175000 |
| 7 | Borrowing and other Labilities1 | 933651 | 796337 | 1848655 | 1506812 |
| 8 | Total Receipts (1+4) | 2686330 | 3042230 | 3450305 | 3483236 |
| 9 | Total Expenditure (10+13) | 2686330 | 3042230 | 3450305 | 3483236 |
| 10 | On Revenue Account of which | 2350604 | 2630145 | 3011142 | 2929000 |
| 11 | Interest Payments | 612070 | 708203 | 692900 | 809701 |
| 12 | Grants in Aid for creation of capital assets | 185641 | 206500 | 230376 | 219112 |
| 13 | On Capital Account | 335726 | 412085 | 439163 | 554236 |
| 14 | Revenue Deficit (10-1) | 666545 (3.3) | 609219 (2.7) | 1455989 (7.5) | 1140576 (5.1) |
| 15 | Effective Revenue Deficit (14-12) | 480904 (2.4) | 402719 (1.8) | 1225613 (6.3) | 921464 (4.1) |
| 16 | Fiscal Deficit [9-(1+5+6)] | 933651 (4.6) | 796337 (3.5) | 1848655 (9.5) | 1506812 (6.8) |
| 17 | Primary Deficit (16-11) | 321581 (1.6) | 88134 (0.4) | 1155755 (5.9) | 697111 (3.1) |
1 Includes drawdown of cash Balance.
Notes:
(i) GDP for BE 2021-2022 has been projected at Rs. 22287379 crores assuming 14.4% growth over the estimated GDP of Rs. 19481975 crore for 2020-2021 (RE).
(ii) Individual items in this document may not sum up to the totals due to rounding off (iii) Figures in parenthesis are as a percentage of GDP.
Deficit Statistics
(In Rs. crore)
| S.no | Particulars | Actuals 2019-2020 | Estimate Budget 2020-2021 | Revised Budget 2020-2021 | Budget Estimate 2021-2022 |
| 1 | Fiscal Deficit | 933651 (4.6) | 796337 (3.5) | 1848655 (9.5) | 1506812 (6.8) |
| 2 | Revenue Deficit | 666545 (3.3) | 609219 (2.7) | 1455989 (7.5) | 1140576 (5.1) |
| 3 | Effective Revenue Deficit | 480904 (2.4) | 402719 (1.8) | 1225613 (6.3) | 921464 (4.1) |
| 4 | Primary Deficit | 321581 (1.6) | 88134 (0.4) | 1155755 (5.9) | 697111 (3.1) |
Direct Tax Proposals
Certain direct tax proposals were introduced, providing relaxation to individual taxpayers and start-ups to some extent. The individual and corporate tax rates for FY 2021-22 (AY 2022-23) were left unchanged.
In a significant move, the limit for tax audits under section 44AB has been increased from Rs. 5 crores to Rs. 10 crores (only where 95% of payments are digitized), providing relief to many corporate houses. The following are other proposed amendments:
- Reduction in time for IT Proceedings: Except in cases of serious tax evasion, assessment proceedings in the rest of the cases shall be reopened only up to 3 years, against the earlier time limit of 6 years.
- National Faceless Income Tax Appellate Tribunal Centre: Provision is made for faceless proceedings before the Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) in a jurisdiction less manner. It will reduce the cost of compliance for taxpayers and increase transparency in the disposal of appeals. Further, it will also help achieve even distribution of work in different benches and ensure efficient administration.
- Constitution of ‘Dispute Resolution Committee’: Those assessed with a taxable income of up to Rs.50 lakh (for small and medium taxpayers) and any disputed income of Rs.10 lakh can also approach this committee under section 245MA. It will prevent new disputes and settle the issue at the initial stage.
- IT relaxation for senior citizens of 75 years age and above: It has been proposed to exempt senior citizens from filing income tax returns if pension income and interest income are their only annual income source, Section 194P has been newly inserted to enforce the banks to deduct Tax on senior citizens more than 75 years of age who have a pension and interest income from the bank.
- Tax incentives to start-ups: The tax holiday for start-ups has been extended by one more year up to 31st March 2022.
- Relaxations to NRI: There is a proposal to notify rules for removing hardship for double taxation.
- Disallowance of PF contribution: In case the employee’s PF contribution was deducted but not deposited by the employer, it will not be allowed as a deduction for the employer.
- Pre-filing of returns to be forefront: Pre-filing will be allowed for salary, tax payments, TDS, etc. Further, details of capital gains from listed securities, dividend income, etc., will be prefilled.
- Advance Tax on dividend income: Advance tax will henceforth be applicable on dividend income only after its declaration. Tax holidays are proposed for aircraft leasing and rental companies.
- Amendment to Section 44ADA: Section 44ADA applied to all the assesses being residents in India. Now onwards, it applies only to the resident individual, Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), or a partnership firm other than LLP.
- Section 80EEA deduction extended: The affordable housing additional deduction was extended till 31st March 2022. The tax exemption has been granted for affordable rental projects.
- Section 43CA stands amended: The stamp duty value can be up to 120% (earlier 110%) of the consideration if the transfer of “residential unit,” which means an independent housing unit is made between 12th November 2020 and 30th June 2021.
Indirect Tax Proposals
A few of the items on which Customs Duty Rates are revised are as follows:
- Basic and Special additional excise duty on petrol and high-speed diesel oil (both branded and unbranded) is reduced.
- The basic customs duty on gold and silver reduced.
- Reduced duty on copper scrap from 5% to 2.5%
- Increased duty on solar inverters from 5% to 20%
- The revised rates will be applicable from 2nd February 2021 onwards.
- Raised duty on solar lanterns from 5% to 15%
- The department will rationalize duty on textile, chemicals, and other products.
- Exemption of Social Welfare Surcharge on the value of AIDC imposed on gold and silver-Therefore, these items would attract surcharge at the normal rate, only on value plus basic customs duty.
- A new initiative called ‘Turant Customs’ will be introduced for faceless, paperless, and contactless customs measures.
- Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess (AIDC) has been newly imposed on petrol and diesel at Rs2.5 and Rs.4 per liter respectively.
- Regarding agricultural products, the customs duty is increased on cotton, silks, alcohol, etc.
- The exemption on the import of leather will be withdrawn as they are domestically produced.
- New tariff items under 2404 11 00 and 2404 19 00 have been inserted in accordance with the upcoming HS 2022 nomenclature Further, NCCD of 25% is prescribed on these tariff items with effect from 1st January 2022.
CGST Act was amended for several provisions as follows:
- Amendment of Section 50 of the CGST Act to provide for a retrospective charge of interest on net cash liability with effect from the 1st July 2017.
- Section 16 amended to allow taxpayers’ claim of the input tax credit based on GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B.
- Section 35 and 44 amended Mandatory requirements of furnishing the GST reconciliation report signed by the specified professional is relaxed by allowing the filing of annual return on a self-certification basis. The Commissioner can exempt a class of taxpayers from the requirement of filing the annual return.
Health
A new centrally sponsored scheme that is PM AtmaNirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana, will be launched with an outlay of about 64,180 crores over 6 years, This will develop capacities of primary, secondary, and tertiary care Health Systems.
Some highlighting points: –
- Supplementary Nutrition Programme and Poshan Abhiyan to be merged and launched as Mission Poshan 2.0
- Outlay ₹64180 crores over 6 years, support for Health and Wellness centers.
- Setting up Integrated Public Health Labs and Establishing critical care hospital blocks.
- Strengthening NCDC and expanding integrated health information portal.
- ₹35000 crores for Covid-19 Vaccine in 2021-22.
- Introduction of National Commission for Allied Healthcare Professionals Bill.
Industry
To Achieve USD 5 trillion economies, Production Linked Initiative Scheme has been announced. It helps to create global manufacturing champions across 13 sectors.
PLI launched to create manufacturing global champions with an amount committed to nearly ₹1.97 lakh crore in the next 5 years starting FY2021-22.
- MITRA Scheme to create world-class infrastructure for global champions in the textile sector, leading to the creation of 7 textile parks over 3 years.
- National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) Project pipeline expanded to 7400 projects.
- Provided Rs. 15,700 crores to support the MSME sector.
Infrastructure
- Aim at developing adequate rail infrastructure by 2030. The objective is to increase the modal share of rail in freight from the current level of 27 percent to 45 percent.
- 100% electrification of Broad-Gauge Routes by 2023
- Indigenously developed automatic train protection system to be launched.
- 139 GW of installed capacity was added during 6 years, connecting additional 2.8 crore households with 1.41 lakh circuit km of transmission lines.
- Revamped reforms-based result-linked power distribution sector scheme will be launched with an outlay of ₹3,05,984 crore over 5 years.
- A hydrogen energy mission will be launched.
- PPP model to be utilized for managing operational services of major ports.
- Subsidy support to promote the flagging of merchant ships.
- Recycling of Ships Act, 2019 enacted, and recycling capacity to be doubled by 2024.
- Ujjwala scheme to cover 1 crore more beneficiaries with 100 more districts under the city gas distribution network.
- Bill to set up a Development Financial Institution will be introduced, provided a sum of Rs20,000 crores, ambition is to have a lending portfolio of at least 5 lakh crores for this DFI in 3 years’ time.
Urban Development
- Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban) for universal water supply in all ULBs (Urban Development Directorate)
- Urban Swachh Bharat Mission with outlay ₹1,41,678 crore over 5 years.
- ₹2,217 crores for 42 urban centers to tackle air pollution.
- Voluntary Vehicle Scrapping policy, to phase out old and unfit vehicles. This will help in encouraging fuel-efficient. Vehicles would undergo fitness tests in automated fitness centers after 20 years in personal vehicles and after 15 years in commercial vehicles.
- Two new technologies, i.e., ‘MetroLite’ and ‘MetroNeo’ will be deployed to provide metro rail systems at a much lesser cost with the same experience, convenience, and safety in Tier-2 cities and peripheral areas of Tier-1 cities.
Financial Reforms
- Rationalized single Securities Markets Code by 2022.
- World-class fintech hub at GIFT IFSC.
- Permanent institutional framework for Corporate bond market.
- SEBI as a regulator and a more significant role for WDRA (Warehouse Development and Regularity Authority) for the development of the commodity market ecosystem.
- Towards investor protection Investor charter was proposed as a right across all financial products.
- Amending the Insurance Act,1938 to increase the FDI limit with safeguards. FDI limit increased from 49% to 74%, with at least 50% of Directors being Independent Directors and a specified percentage of profits being retained as a general reserve
- 10% disinvestment in Life Insurance Corporation is proposed, to raise Rs. 1 lakh crore from it.
- Asset Reconstruction Company Limited and Asset Management Company to resolve stressed assets problem of PSBs.
- Recapitalization of Rs. 20,000 crore is proposed in 2021-22 for Public Sector Bank.
- Scheme of Stand-Up India for SCs, STs, and women, reduce the margin money requirement from 25% to 15% and also include loans for activities allied to agriculture.
Agriculture and Fisheries
- Extending coverage of SWAMITVA Scheme to all states/UTs Up till now, about 1.80 lakh property-owners in 1,241 villages have been provided cards.
- To provide adequate credit to our farmers, Government enhanced the agricultural credit target to Rs. 16.5 lakh crores in FY22.
- Expansion of Operation Green scheme to include 22 perishable products.
- Rural Infrastructure Development Fund increased from Rs. 30,000 crores to Rs. 40,000 crores.
- ‘Operation Green Scheme’ that is presently applicable to tomatoes, onions, and potatoes, will be enlarged to include 22 perishable products.
- 1000 more mandis to be integrated with e-NAM.
- 5 major fishing harbors – Kochi, Chennai, Visakhapatnam, Paradip, and Petuaghat – will be developed as hubs of economic activity.
- To promote seaweed cultivation, Multipurpose Seaweed Park to be established in Tamil Nadu.
Migrate Worker and Labour
- One Nation One Ration Card scheme launched to claim their rations anywhere in the country. Those staying away from their families can partially claim their ration where they are stationed. One Nation One Ration Card plan is implemented by 32 states and UTs, reaching about 69 crores beneficiaries.
- A portal to be launched for the gig, building, and construction workers. This will help formulate Health, Housing, Skill, Insurance, Credit, and food schemes for migrant workers.
- Scheme of Stand-Up India for SCs, STs, and women, reduce from 25% to 15% and also include loans for activities allied to agriculture.
- Provided Rs. 15,700 crores to support the MSME sector.
Education
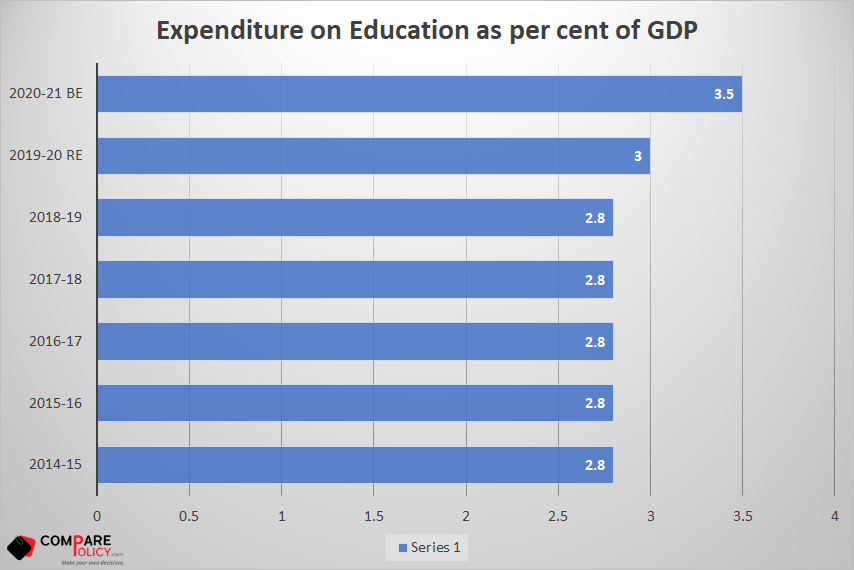
- 100 new Sainik Schools will set up in partnership with NGOs/ private schools/states.
- Propose to set up a Central University in Leh (Ladakh).
- Propose to establishing 750 Eklavya model residential schools in tribal areas.
- Revamped the Post Matric Scholarship Scheme, for the welfare of Scheduled Castes, Allotting Rs 35,219 crores for 6 years till 2025-2026.
- Realigning National Apprenticeship Training scheme for graduates and diploma holders in Engineering. Over Rs. 3,000 crores will be provided for this.
- Partnership with UAE and Japan in the area of skill development and recognition.
Research and Development
- National Research Foundation with an outlay of ₹50,000 crores over 5 years.
- National Language Translation Mission to boost internet access in major Indian languages.
- Deep Ocean Mission for ocean exploration and biodiversity conservation, Allocated more than Rs 4,000 crores, over 5 years.
Fiscal Position
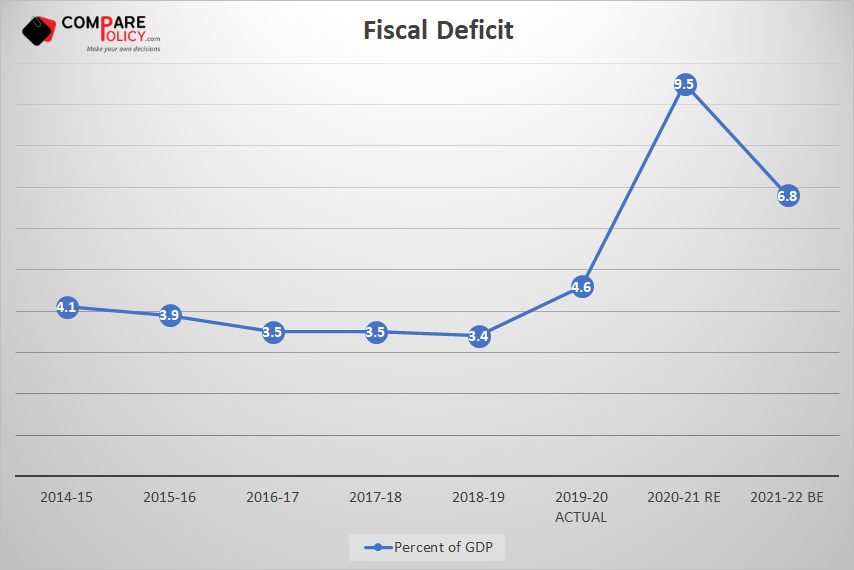
- Allowing a normal ceiling of net borrowing for the states at 4% of GDP for 2021-22.
- Additional Borrowing ceiling of 0.5% of GDP subject to conditions.
- NSSF loan to FCI for food subsidy to be replaced by making budget provisions.
- 1,18,452 crores as Revenue Deficit grant to 17 states in 2021-22.
To access Full Budget, Please click Here
Compare all arrangements with comparepolicy.com and pick the most appropriate Life protection for yourself.

